Shoulder Arthroscopy
Shoulder arthroscopy is a commonly performed key-hole surgery of the shoulder. It is used to visualise, diagnose, and treat various problems inside the shoulder joint and in the space surrounding the rotator cuff.
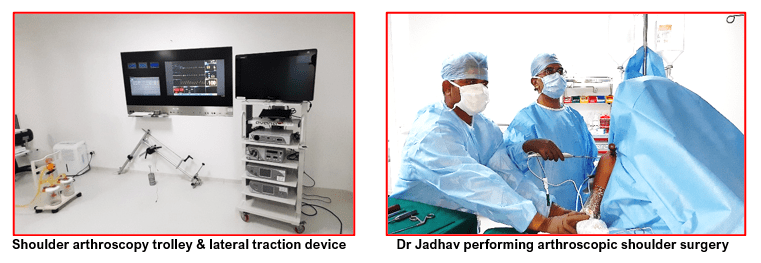
The surgeon first makes a portal (tiny keyhole) around the shoulder joint. He then inserts an arthroscope (small telescope), with attached light source and a video camera, to look into the shoulder joint. He then creates additional 2 to 3 portals as needed and inserts specialised instruments through them for various surgical steps.
The images from the shoulder joint are seen on a large screen monitor which helps the surgeon to diagnose or treat multiple shoulder problems as needed under arthroscopic vision. Images of the shoulder pathologies and videos of the surgery performed can also be recorded for documentation purposes.
 Shoulder arthroscopy is a relatively safe procedure and a majority of the patients get discharged from the hospital on the same day of surgery or the next day.
Shoulder arthroscopy is a relatively safe procedure and a majority of the patients get discharged from the hospital on the same day of surgery or the next day.
Dr Anand Jadhav has 25 years of surgical experience. He has undergone highly advanced and specialised training in arthroscopic surgeries of the shoulder joint across multiple centres in the UK, Europe and the USA. He prefers to do arthroscopic shoulder surgeries at hospitals that have all the necessary specialised equipment along with trained support staff. This helps him in providing best outcomes to the patients.
Shoulder arthroscopy, being a minimally invasive procedure, offers several advantages:
- Smaller scar which are cosmetically better
- Less tissue injury
- Minimal pain
- Minimal swelling
- Shorter hospital stay
- Faster recovery
- Ability to dynamically assess tissues when probed or put under tension.
- Better visualisation of certain pathologies compared to open surgery.
The shoulder joint is vulnerable to a variety of injuries as well as non-traumatic lesions.
The most common shoulder problems where shoulder arthroscopy may be recommended for diagnosis and treatment are:
- Shoulder instability and recurrent dislocations
- Partial or complete tears of the rotator cuff tendons
- Tears of the long head of biceps tendon at its insertion (SLAP Tears)
- Biceps tendinitis, distal tendon tears and dislocations
- Subacromial bursitis and subacromial impingement
- Acromioclavicular (AC) joint dislocations and osteo-arthritis
- Shoulder (glenohumeral) joint osteo-arthritis
- Calcific tendinitis
- Adhesive Capsulitis (Frozen shoulder)
- Loose bodies due to any reason or synovial tissue lesions – e.g synovectomy for rheumatoid arthritis
- Infected shoulder joint (septic arthritis of the shoulder)
- Certain fractures of the shoulder region: isolated fractures of the greater tuberosity, lesser tuberosity or the glenoid.
Steps involved in shoulder arthroscopic surgery are:
- Shoulder arthroscopy is performed in a suitably counselled patient with proper consent.
- This surgery is done under general anaesthesia with interscalene block. Our anaesthetist will decide the best method for you depending on your age and health condition.
- Patient are operated either in the beach chair (sitting) position or in the lateral position (lying down sideways with arm in a traction device). The choice of position depends upon the type of surgery to be performed and the surgeon’s training.
- The shoulder to be operated is thoroughly scrubbed and the surgical pre-operative sterile skin preparations are done. The surgeon will make a small keyhole incision (portal) around the back of the shoulder joint through a pre-marked site.
- An arthroscope (a narrow telescope) with an attached light source and a tiny video camera on the end, is inserted through one of the portals to view the shoulder joint. The structures inside the shoulder are visible on a large video monitor in the operating room.
- Sterile normal saline solution is injected into the shoulder to distend it which pushes apart the various internal structures to provide a clear view and make more room to work.
- The surgeon systematically examines all the structures inside the shoulder joint to assess the cause of the problem and takes detailed photo images for documentation.
- Once the diagnosis is made or confirmed, additional portals are created as required. Then surgical instruments such as probes, scissors, motorized shavers, or radiofrequency probes (similar to lasers) are inserted through these portals, and the necessary work is performed based on the findings.
- The procedures performed arthroscopically may include any of the following:
- Repair of a torn labrum for shoulder instability and recurrent dislocations (Bankart repair)
- Repair or debridement of superior labral lesions (SLAP Repair)
- Relocation (Biceps tenodesis), tenotomy or debridement of tendon of the long head of biceps for tears, dislocations or tendinitis
- Rotator cuff repairs of complete tears of the rotator cuff tendons
- Debridement of partial tears of the rotator cuff tendons
- Capsular release for adhesive capsulitis (frozen shoulder)
- Removal of loose fragments of bones, any other loose bodies or calcium deposits
- Removal of inflamed synovial tissue (Synovectomy) e.g. for rheumatoid arthritis
- Removal of subacromial bursa and decompression of subacromial space to prevent impingement (Subacromial bursectomy + Subacromial decompression)
- Making small holes in the damaged articular cartilage to stimulate cartilage regrowth (Microfractures)
- Fixation of certain fractures around the shoulder (tuberosities or glenoid fractures)
- After completion of the arthroscopy, the shoulder joint is carefully examined for any bleeding or any other damage to surrounding tissue. Any bleeding is controlled with RF device and its wand.
- The joint is washed out with the normal saline irrigation to clear any debris. The saline fluid is then drained from the shoulder joint as much as possible.
- Finally, the incisions are closed with sutures or sterile sticky tapes and covered with sterile dressing pads. Compression bandages are given.
Patient is given a shoulder sling and then shifted to the recovery room for observation.
- Most patients are discharged the same day or the next day after shoulder arthroscopy. Recovery after the surgery depends on the type of procedure performed. Recovery from simple procedures is often fast. However, recovery from complicated or complex procedures takes a little longer. Patients are counselled pre-operatively about their recovery time which can be between 2 to 6 weeks for simple procedures and 6 to 12 weeks for complex procedures.
- Recovery from shoulder arthroscopy is much faster than that from an open shoulder surgery.
- Pain medicines are prescribed to manage pain for the first 3 to 5 days. Thereafter they are taken only if required.
- Ice packs are given 4 to 5 times a day and carried on for 1 to 2 weeks.
- Physiotherapist visits patients prior to their discharge. Simple shoulder pendulum exercises are taught and then carried on by patient at home for 2 to 4 weeks. For complex surgeries, patients may need to be seen by a physiotherapist on a regular basis and for longer duration of about 2 to 3 months. This type of formal rehabilitation program ensures successful and faster recovery.

- Simple shoulder sling or specialised shoulder braces may be needed for 2 to 6 weeks post-surgery depending upon complexity of surgery performed. Patients are given instruction for care of the sling and avoidance of wound problems due to sweating or itching.
- Surgical wounds are checked at 10 days post-surgery. All dressings and sutures, if any, are removed at this visit.
Shoulder arthroscopy is a safe procedure and complications are rare.
Complications that may arise from shoulder arthroscopic surgery are bleeding into the shoulder joint, infection, swelling, shoulder stiffness, bruising around shoulder joint, damage to surrounding nerves, blood vessels, joint cartilage, tendons, ligaments and rarely, continuing shoulder problems.
Book An Appointment
Private Clinics : Locations & Directions
London Joints Clinic (Pune)
Address
Office S 5, 2nd Floor, North Block, Sacred World Mall,
Opp Sacred Heart Township, Near Jagtap Chowk,
Wanawadi, Pune 411040
Monday, Wednesday & Friday 7 PM to 9 PM
Sunday 11 AM to 1 PM
Appointments
London Joints Clinic ( PCMC )
Address
C/O Dr Nitin’s Physio Clinic,
Opp. Brahma Hotel,
Near Akurdi Post Office,
Vivek Nagar,
Akurdi,
Pune 411035
Saturdays only 4.30 PM to 7.30 PM
Appointments
Hospitals OPDs : Locations & Directions
Manipal Hospital

Address
Manipal Hospital, Opp D Mart, Baner-Mhalunge Road, Baner, Pune 411 045
Monday to Saturday 11 AM to 4 PM
Appointments
Contact us
Dr Anand Jadhav has a centralised appointment system for all locations across various hospitals and clinics in Pune & PCMC areas
Appointment Bookings & Requests can be made by any method :