Hip Impingement &
Labral Tears
Hip impingement, also called femoro acetabular impingement (FAI), refers to the abnormal contact and friction between the bones in the hip joint during certain movements of the hip. This impingement is usually caused by an imperfect fit between the head of the femur (the ball) and acetabulum (the socket). As a result, the labrum, that surrounds the acetabulum and stabilises the joint, gets pinched when the bones rub together.
Hip impingement causes damage to the articular cartilage, significant pain and can lead to premature arthritis of the hip.
The nature and extent of the impingement can vary depending on what part of the joint is out of place and which surrounding tissues are affected.
There are 3 types of Hip Impingements:
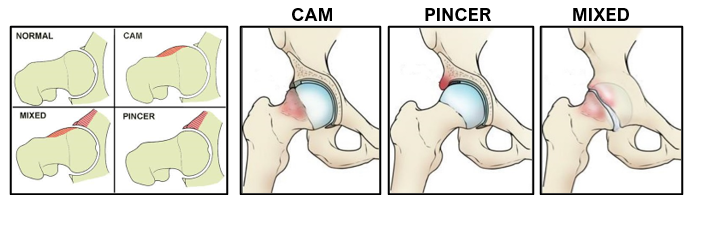
1) Cam Hip Impingement
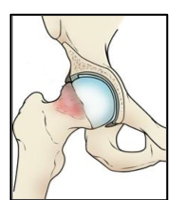
A cam hip impingement arises when the head of the femur isn’t sufficiently rounded to fit within the acetabulum and labrum seal. This non-spherical head abuts against the anterior (front portion) acetabulum and creates friction on movements of the hip joint. Because of the malformation, bone spurs grow on the unrounded end of the femur. These spurs strike the labrum and grind the articular cartilage inside the joint whenever the hip gets rotated. Such patient’s symptoms are worsened by prolonged upright sitting and internal rotation in flexion at the hip joint.
2) Pincer Hip Impingement
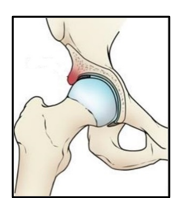
A pincer hip impingement occurs when the rim of the acetabulum hangs over the head of the femur Generally there is anterior over coverage of the acetabulum leading to acetabular retroversion.
This overhanging acetabulum abuts against the femoral head neck junction during hip flexion and crushes the acetabular labrum and causes damage to the hip joint. Where pincer type impingement predominates, abduction and external rotation movements may be more troublesome.
3) Mixed (COMBINED) Hip Impingement
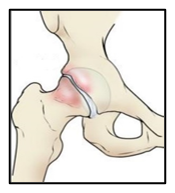
This type of hip femoro acetabular impingement is a combination of both Cam-type and Pincer-type hip femoro acetabular impingement.
FAI develops early and may go unnoticed throughout your life. It usually affects both hip joints and may happen in combination.
The labrum is a ring of flexible cartilage that sits on rim of the bony socket of the hip joint. The labrum has many functions including shock absorption, joint lubrication, pressure distribution, and aiding in stability of the hip joint by deepening the socket.
The labrum of the hip may tear, causing hip pain and instability.
There are two general types of hip labral tears: Degenerative and Traumatic
A degenerative tear of hip labrum occurs as a result of repetitive use and activity. This type of tear is often associated with femoro acetabular impingement (FAI). As the hip flexes (bends up) and rotates the labrum may be pinched and can becomes shredded. Patients are typically active, often taking part in sports such as running, kick boxing, mountain biking and horse riding
A traumatic tear of the hip labrum occurs due to an acute injury as a result of a sports injury, fall, or accident. The pattern of injury is commonly associated with sudden, twisting manoeuvres that cause immediate pain in the hip.
The labrum is a ring of flexible cartilage that sits on rim of the bony socket of the hip joint. The labrum has many functions including shock absorption, joint lubrication, pressure distribution, and aiding in stability of the hip joint by deepening the socket.
The most common symptoms of hip impingement are pain, stiffness and limp.
- Patients will often experience pain in the groin with deep flexion or rotation of the hip during certain activities. Hip-related pain is not always felt directly over the groin. It may also be felt on the outer aspect of the thigh, the buttock or traveling down the leg. The pain often presents as a dull ache, but can turn into a sharp, stabbing pain during physical activity and as the condition worsens.
- If the condition has been present for some time, there may also be inflammation of the tissues surrounding the hip such as on the outer side of the hip (trochanteric bursitis), the groin muscles (adductor tendonitis) or inflammation of tendons in front of the hip.
- Eventually, as the damage continues, the patient may begin to develop more arthritic symptoms such as a dull ache in the groin, increasing stiffness and limp whilst walking.
Hip impingement is diagnosed based on detailed medical history, thorough clinical examination and pain provoking manoeuvres, X-rays of the hip joints, MRI & CT scans of the hips.
X-rays will show anatomy of the hip joint, any alteration in the shapes of femoral head or the acetabulum and any presence of arthritic changes.
MRI shows the extent of damage to the acetabular labrum, the joint cartilage, any inflamed bursa and presence of fluid within the joint.
CT scan is performed to study the bony detail of the hip. A computer-generated 3-D model of the patient’s hip joint is produced so that the shape of the hip can be studied pre-operatively. This assists in planning for accurate corrective surgery. New motion analysis software also helps in operative planning.
Hip impingement can be managed with conservative (non-surgical) and surgical methods
All patients are initially managed with conservative approach which includes:
- Resting the affected hip
- Modifying patient lifestyle and avoiding pain producing activities
- Specialised hip physiotherapy to strengthen the muscles supporting the hip joint.
- Using anti-inflammatory and painkiller medications as needed.
- An injection of the hip joint with local anaesthetic can provide some relief as well as diagnostic information in patients with symptoms which are unresponsive to treatment.
Surgical Treatment for Hip Impingement (FAI):
For definitive treatment, femoro acetabular Impingement (FAI) can be addressed with surgery to improve the shape of the hip. The surgery aims to correct the bony deformity before there is irreversible structural damage to the hip joint. These hip preserving surgeries reduce pain, improve hip range of motion and allow patients to lead an active lifestyle.
- In many cases this can be done by Hip arthroscopy.
Using minimally invasive keyhole surgery and specialised instruments, the abnormal bumps on the femoral head and neck regions are smoothened out to reshape it and any labral tears are either debrided (cleaned) or repaired with special anchors. Hip arthroscopy is highly specialised and technically difficult surgery but can achieve excellent results if carried out correctly and on the right patient.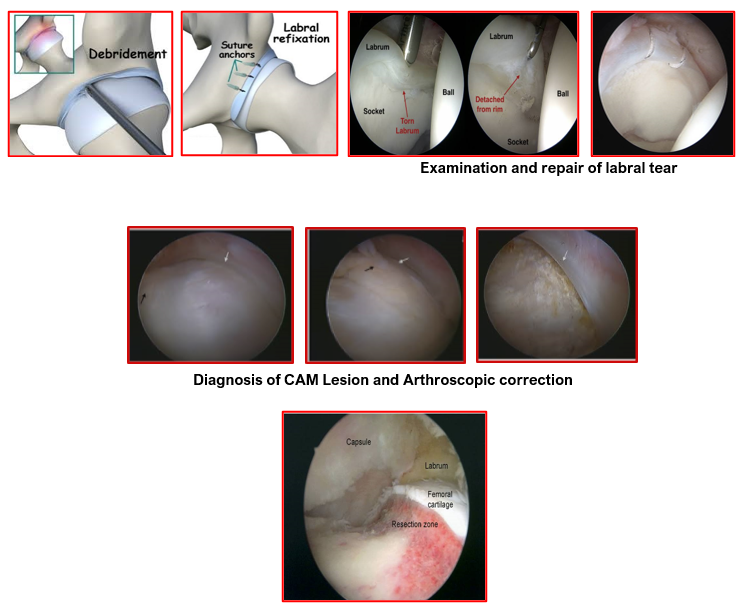
- In few cases the bony deformities are large or awkwardly situated. Hip arthroscopic techniques may not be reliable to adequately reshape such bones. In such cases the operation may be performed using a ‘mini-open’ or open technique.
In cases where there is progression to advanced arthritis and symptoms deteriorate, hip replacement surgery is recommended for pain relief and improved quality of life.
Book An Appointment
Private Clinics : Locations & Directions
London Joints Clinic (Pune)
Address
Office S 5, 2nd Floor, North Block, Sacred World Mall,
Opp Sacred Heart Township, Near Jagtap Chowk,
Wanawadi, Pune 411040
Monday to Saturday
6 PM to 9 PM
Appointments
Hospitals OPDs : Locations & Directions
Jupiter Hospital (Baner)

Address
Lane 3, Baner- Balewadi Road,
Prathamesh Park,
Baner, Pune 411 045
Monday to Saturday 11 AM to 4 PM
Appointments
Contact us
Dr Anand Jadhav has a centralised appointment system for all locations across various hospitals and clinics in Pune & PCMC areas
Appointment Bookings & Requests can be made by any method :