Hip Arthritis and
Joint Replacement
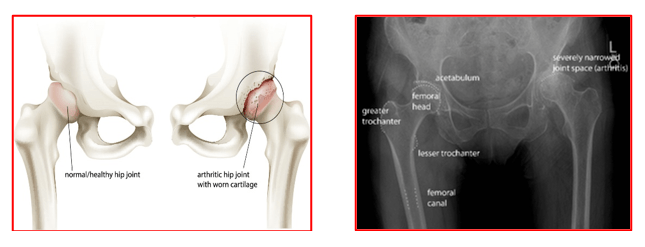
Hip arthritis is a condition in which the articular cartilage of the hip joint gets damaged due to any reason. This affects the cartilage of the femoral head and the acetabular socket leading to joint inflammation, pain and difficulty in mobilising. In the later stages, the joint surfaces get completely worn out, the bones become deformed and the joint function deteriorates.
Hip arthritis can be primary (without any predisposing factor) or secondary (due to some predisposing factor)
Primary arthritis is generally age related ‘wear and tear’ of the hip joint.
It may have a genetic link and is more common in caucasian population.
Secondary arthritis occurs due to:
- Inflammatory arthritis like Rheumatoid arthritis
- Post traumatic – with fractures injuring the joint surfaces
- Infection - can destroy the joint cartilage and lead to arthritis
- Obesity - puts excessive stresses on the joint surfaces causing early wear and tear.
- Overuse of hip joints - as in sports or heavy physical labour
- Developmental problems
Patients with hip arthritis will have following symptoms:
- pain in groin while walking or even at rest.
- difficulty in walking far
- stiffness and limp
- difficulty in getting in and out of a chair or sitting on floor
- difficulty with crossing legs
- difficulty in bending forwards and disturbed sleep.
The clinical diagnosis of hip arthritis is made based on patient’s complaints, detailed medical history, thorough clinical examination and appropriate investigations.
X-rays of the hip joint help in confirming the diagnosis and severity of arthritis. The surgeon can then decide when a hip replacement surgery is appropriate for the patient.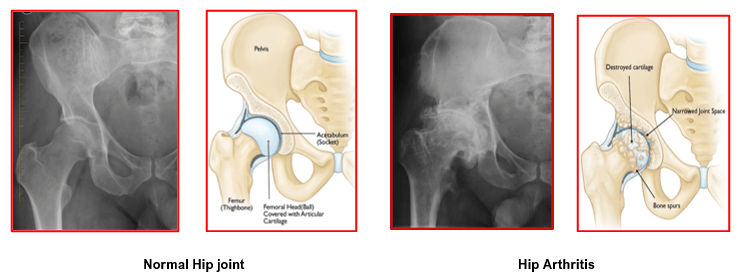
In some cases, additional investigations like MRI or CT scans are also used to assist the diagnosis and help in the pre-operative planning of hip replacement surgery.
The non-surgical treatment options for management of hip arthritis are:
- Weight Loss
Probably one of the most important, yet least commonly performed treatments. The less weight the joint has to carry, the less painful activities will be. Roughly loosing 1 kg means 3 kg less burden on the joint. Being obese can make surgery difficult.
- Activity modification
Patients need to learn to avoid activities that induce pain. Some modifications will help them to do routine activities without pain.
- Walking Aids
Use of a walking stick or a single crutch in the hand opposite the affected hip will help decrease the demand placed on the arthritic joint.
- Physiotherapy
Strengthening of the muscles around the hip joint may help decrease the burden on the hip joint. Exercises will help in maintaining the range of motion as well as function of the hip joint. Doing regular exercises will not worsen the arthritis. In active patients the recovery after surgery is also rapid.
- Anti-inflammatory & Pain-killer Medication.
These are helpful to treat pain and inflammation. Different types are available and are prescribed taking into consideration patient’s safety and pain levels. Medications should be taken as per doctors’ instructions only.
- Chondroprotective agents
Glucosamine and chondroitin sulphate are considered as ‘chondroprotective agents’ or ‘neutra-ceuticals’. They may slow down the process of arthritis and have some pain-relieving effect. For best results both these medications should be taken together in appropriate dosage.
- Visco-supplementation
These injections have hyaluronic acid. They are clear liquids which increase the viscosity of joint fluid and also the elasticity of the joint cartilage. They improve the lubrication and reduce friction between raw end of arthritic joint surface. They may cause healing of small cartilage defects. The pain reliving effect may last for 6 to 12 months. These injections are most useful for mild to moderate arthritis. These injections are available as a single shot or multi- injections.
Hip replacement surgery is advised for the following problems:
- Osteoarthritis - this is the most common form of arthritis and occurs when connecting tissue between the joint is damaged. Because the two ends of the joint rub together in the absence of the connective tissue, one would feel the pain while moving, resting and sleeping
- Rheumatoid arthritis -this is caused by the immune system attacking the lining of the joint, resulting in pain and stiffness. Joints get painfully swollen and may need to be replaced.
- Fracture of the neck of femur (thigh bone) - this causes a loss of blood supply to the head of the femur and may also lead to crumbling (avascularnecrosis - AVN) of the ball of the hip joint.
- Avascular necrosis (AVN) of the hip for any other reason
- Paget's disease of bone -this affects bone growth and can make bones weak and deformed,
- Bone tumours
- Other hip joint injuries and fractures
Hip replacement is the most effective treatment for an arthritic hip joint that cannot function adequately and painlessly. Surgery is advised based on the extent of patient’s pain, disability and general health status.
Hip replacement is recommended if a patient has:
- Hip pain that limits everyday activities such as walking or bending.
- Continuous hip pain during day or night
- Stiffness in a hip that limits ability to move or lift affected leg
- No improvement in hip pain despite regular pain-killer medications, restriction of daily activities or use of a walking stick
- Harmful or unpleasant side effects from pain-killer medications
- X-rays showing advanced stages of hip arthritis.
Even when a hip replacement is needed, some medical problems may lead your surgeon to
recommend that you not have it done. Some of these problems are:
- Morbid obesity (weighing over 300 pounds)
- Very weak quadriceps, the muscles in the front of your thigh.
- Weak quadriceps could make it very hard for you to walk and use your hip.
- Unhealthy skin around the hip
- Severe mental dysfunction
After hip replacement surgery, patients can expect the following:
- Dramatic reduction of hip pain
- Major improvement in performing normal activities of daily living
- Most patients with stiff hips before surgery will regain near-normal motion and nearly all have improved motion.
- The person will not be able to do more than he/she could do before the hip problem developed
- The artificial hip may allow you to return to active sports or heavy labour under surgeon’s instructions.
- The surgeon will ask you to discontinue jogging and high-impact sports, for the rest of your life.
- Patients will be asked to avoid specific positions of the joint that could lead to dislocation.
An artificial joint will also wear out over time, even with regular use. High-impact activities or overweight may accelerate the wear of and cause this artificial joint to loosen and become painful.
The key is to choose a specialist who has learnt hip replacement from reliable institutes and is willing to discuss his results with you.
Look for a specialist who knows different surgical modalities like total hip joint replacement, hip resurfacing, revision hip joint replacement and will work with you to find the best treatment for you as an individual.
- A complete physical examination is done 5 to 7 days before your surgery by a general physician. This helps in assessing your medical fitness and also identifying problems which can delay your operation e.g. High blood pressure or high sugar levels.
- Blood and urine samples are taken for tests
- ECG and Chest x-ray are done. Echocardiography may be needed in certain patients.
- There should not be any dental, skin, chest or urine infection. Open wounds should be allowed to heal.
- You may be advised to donate your own blood prior to surgery. It will be stored in the event you need blood after surgery.
- Certain type of medications will need to be stopped before surgery to avoid bleeding problems.
- You must discuss all your regular medications with Dr Jadhav so that he can advise you which one to stop before surgery.
Get informed - Find out about your standard of room in the hospital, whether a relative can stay with you overnight, what kind of anaesthesia (general or spinal) will be given to you and any other information relevant to your surgery.
Arrange home help - Line up a relative or a nurse or an attendant to help you at home for some weeks after coming home from hospital.
Arrange for transport - Arrange for someone to take you to and from the hospital in a comfortable vehicle.
Prepare your home - Prepare your bed and chair where you would be spending most of your time after the surgery.
In case you are using Indian style toilet, please arrange for a raised seat.
Clean up - Before going into hospital have a good long bath or shower, cut and clean your nails. Put on freshly washed clothes.
This helps prevent unwanted bacteria going with you to hospital and complicating your care.
This is decided by the anaesthetist after your health status and investigations have been checked. The anaesthesia can be general or regional. The anaesthetist will discuss these matters with you and choose the best option.
Generally hip replacement surgery is done under spinal or epidural anaesthesia.
The area below the waist is made numb for the operation. After the spinal or epidural anaesthesia is given, patient can choose to remain fully awake or have a sedative injection.
Epidural anaesthesia is continued (via a tiny catheter tube and a syringe pump) for next 2-3 days for pain control. It helps in starting exercises in bed without pain and gives patient confidence about physiotherapy.
The actual surgical procedure usually takes about 1-2 hours.
However, pre-operative preparations as well as wake-up time may make your operating room and recovery room stay longer.
Uncemented hip replacement takes shorter time whilst cemented hip replacement take longer.
- Hip replacement surgery is a surgical procedure to reconstruct the normal ball and socket of hip joint.
- The surgeon removes the damaged cartilage from the acetabulum (socket) of the hip joint and inserts a new socket.
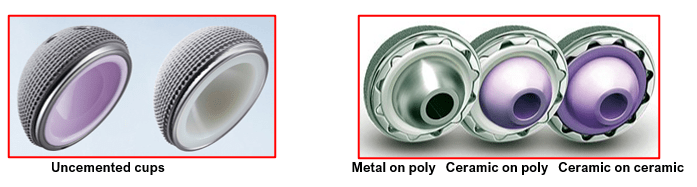
- These sockets are made up of either a durable plastic (Ultra high molecular weight polyethylene) or a metallic shell.
- Plastic socket shells are fixed with special glue called bone cement (poly methyl methacrylate) which fills the area between the prosthesis and the bone. It provides stable fixation once it becomes hard.

- Metallic socket shells are inserted without bone cement (un-cemented) by press fit technique.
- They have an outer specialized porous coating which allows bone to grow within it to provide stability.
- Screws can also be used for additional fixation of un-cemented sockets.
- The lining used inside these metallic shells can be plastic, metallic or ceramic.
- The damaged cartilage of femoral head (ball) and a small segment of upper part of femur (thigh bone) are removed.
- A hollow is then created to insert the new implant (Stem) into the thigh bone.
- Highly polished smooth stem made of metallic alloy or stainless steel is inserted with bone cement.
- Newer un-cemented stems with specialized porous coating are inserted without bone cement by press fit technique.
- Bone grows into the porous coating to provide fixation and stability.
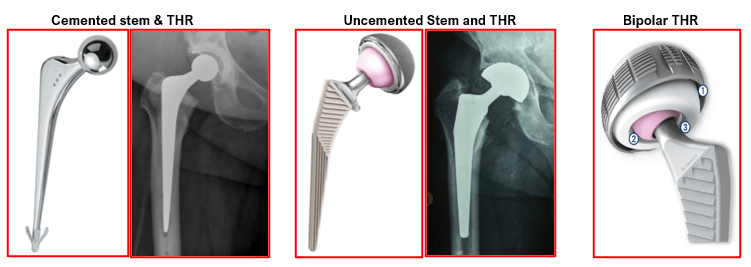
- A highly polished smooth metallic or ceramic ball is then put on top of the stem.
- The stem with its new ball is then relocated into the new socket to bring back the alignment and function of the hip joint.
- Un-cemented implants are used in younger patients with strong bones.
- Cemented implants are used in elderly patients and in those with weak bones.
Dr Jadhav will select the best option for you based on your situation.
The physiotherapist will help you to get up and walk about as quickly as possible. 1-2 days after surgery you may be able to sit on the edge of the bed, stand, and even walk with help. You have to use a walker initially and then move onto crutches if your progress is satisfactory. It is normal to experience discomfort while walking and exercising. Your legs and feet may be swollen.
A physiotherapist will teach you exercises to help strengthen the hip and explain what should and shouldn't be done after the operation. They will teach you how to bend and sit so as to avoid damaging your new hip.
Most patients will need to use crutches or a walker for about 4-6 weeks or until instructed otherwise by their physiotherapist.
The joint pain that you had before the surgery will go away, but there will be different type pain due to the operation. This post-operative pain will be temporary and is well controlled with pain-killer medications either in the form of injections or tablets. My team is very efficient in pain management. This enables patients to get excellent pain relief. They rehabilitate smoothly and quickly.
Your hospital-stay will be around 3 to 4 days depending on your fitness and progress following the operation.
It is quite normal for you to feel very tired in the beginning. As this is a major operation and muscles and tissues surrounding your new hip will take time to heal. Home help is recommended for the first few weeks.
Your physiotherapist will instruct you about simple home exercises and also the frequency of doing these. Patients should follow these instructions to avoid over-exercises which can cause more pain or swelling.
Sutures or skin staples are removed 14 days after surgery. Your wound will be checked prior to discharge and the dressing will be changed. This wound dressing can be left undisturbed till the time of suture removal.
You can have a bath or shower generally 2 weeks after the operation when wounds have been checked for healing and all sutures or skin staples have been removed.
After hip replacement surgery you should contact Dr Jadhav if you notice any fever or chills (38° C or 100.4° F), persistent warmth or redness around the hip, Discharge (leakage) from wound, persistent or increased in pain in the hip region, calf muscle pain and shortness of breath.
The patient should be able to get rid of crutches by 4 to 6 weeks and feel more or less normal by three months. Normal daily activities of living become easier. Always take your surgeon and physiotherapist’s advice before beginning an activity.
It depends on your progress, but usually after about 4 to 6 weeks. You need to have regained sufficient muscle control and power of operated leg by this time. Please consult Dr Jadhav for further advice.
It depends on your job and recovery from surgery. Most office-type workers can resume work in 4-6 weeks. Those who have undergone more complicated surgery can take between 6-12 weeks after surgery and there may be extra precautions and restrictions.
Usually 6 weeks after your hip replacement, you need to meet Dr Jadhav for a check-up. He will examine your operation site, your walking, your balance and muscle strength.
Dr Jadhav will then see you at 6 months and 1 year following your surgery. X-rays will be done during these visits to check all is well. Subsequent follow-ups are advised after 5 and 10 years with new x-rays of your hip replacement to see for any signs of loosening.
It takes about 3 months for the hip to recover to a point where you are back to full activity. Obviously, some patients recover faster and others more slowly depending upon age, health status, personal motivation, and response to rehabilitation.
The purpose of hip replacement surgery is to relieve pain, allowing you to return to a high level of function. This means that most activities are okay once you have completely healed. However, you must avoid "impact" type of activities, such as running, aerobics, cutting or pivoting sports, or other activities that place a high degree of stress on the hip. Walking, bicycling, swimming, cross-country skiing, golf, and bowling are often okay.
If you were finding sex difficult before because of pain, you may find that having the operation gives your sex life a boost. Your surgeon can advise when it is OK to have sex again but as a rule of thumb, so long as you are careful, it should be fine after six to eight weeks. You should avoid vigorous sex and more extreme positions.
Hip replacement is the most effective treatment for an arthritic hip joint that cannot function adequately and painlessly. Surgery is advised based on the extent of patient’s pain, disability and general health status.
Hip replacement is recommended if a patient has:
- Hip pain that limits everyday activities such as walking or bending.
- Continuous hip pain during day or night
- Stiffness in a hip that limits ability to move or lift affected leg
- No improvement in hip pain despite regular pain-killer medications, restriction of daily activities or use of a walking stick
- Harmful or unpleasant side effects from pain-killer medications
- X-rays showing advanced stages of hip arthritis.
These days, most of the artificial hips last for 15 to 20 years. If the patient is young, he/she may need another new hip at some point in life.
Revision hip replacement surgery is more complicated and time-consuming to perform than a first hip replacement and complication rates tend to be higher. Hence, the patient must avoid high-impact sports and becoming obese to prevent a revision very soon. With improvement in techniques and experience, revision surgery is much more successful than it used to be, the new hip lasts for 10 to 15 years or more.
Possible risks during hip surgery are:
Risks for any anaesthesia are:
Allergic reactions to medicines
Breathing problems
Risks for any surgery are:
Blood clots in the legs (DVT- deep vein thrombosis) that may travel to the lungs (PE- pulmonary embolism)
Infection, including in the lungs, urinary tract, and chest
Bleeding
Heart attack or stroke during surgery
Some risks of this surgery are:
Dislocation of the artificial joint
Infection of the hip joint
Wear of the artificial joint
Loosening of the artificial joint over time
Limb length alteration
Pneumonia
Extra bone growth that can cause stiffness
Allergic reaction to the artificial joint
Injury to nerves or blood vessels
People, who have prosthesis, such as an artificial joint, need to carefully protect themselves against infection. You should carry a medical identification card in your wallet that says you have prosthesis. You may need to take antibiotics before any dental work or invasive medical procedures.
Yes, there are a number of things you need to be aware of. Your new hip is designed to eliminate pain and increase function. Certain movements place undue stress on your new hip and may lead to dislocation. For your safety, these should be avoided. This is especially true during the first few months after your surgery.
Here is an outline of the precautions you should follow after surgery.
Always sit in a chair with arms. Avoid sitting on low chairs or sofas. Instead sit in a high-chair or place a firm cushion on your furniture. Use the armrests on the chair to assist you getting up.
All furniture that you sit or lie on must be at least 18 inches off the floor.
Do not cross your legs. Always sit with your legs 3 - 6 inches apart. Use a pillow between your legs when sleeping.
Have a pillow between your legs when turning in bed.
Avoid Indian toilet seats. Use a commode or a commode chair. When using a public restroom, you should use the handicapped facilities to ensure adequate toilet height.
Use a shower only. Do not use bathtub until your surgeon tell you when it is safe. Use a seat in tub for shower.
Do not reach down to put on shoes and socks. You may want to get a long handle shoehorn.
Avoid stooping, squatting or bending forward excessively for the first 6 weeks. Use a grabber if you need something very low.
Do not turn your knee, hip, or foot inward when sitting, standing, or lying down.
Avoid sudden twisting or pivoting movements of your hip.
In addition, when visiting physicians and dentists it is important that you inform them that you have a total joint replacement. You will need antibiotics for certain dental and medical procedures, ask your doctor for a medical alert card, if you don't already have one.
Book An Appointment
Private Clinics : Locations & Directions
London Joints Clinic (Pune)
Address
Office S 5, 2nd Floor, North Block, Sacred World Mall,
Opp Sacred Heart Township, Near Jagtap Chowk,
Wanawadi, Pune 411040
Monday, Wednesday & Friday 7 PM to 9 PM
Sunday 11 AM to 1 PM
Appointments
London Joints Clinic ( PCMC )
Address
C/O Dr Nitin’s Physio Clinic,
Opp. Brahma Hotel,
Near Akurdi Post Office,
Vivek Nagar,
Akurdi,
Pune 411035
Saturdays only 4.30 PM to 7.30 PM
Appointments
Hospitals OPDs : Locations & Directions
Manipal Hospital

Address
Manipal Hospital, Opp D Mart, Baner-Mhalunge Road, Baner, Pune 411 045
Monday to Saturday 11 AM to 4 PM
Appointments
Contact us
Dr Anand Jadhav has a centralised appointment system for all locations across various hospitals and clinics in Pune & PCMC areas
Appointment Bookings & Requests can be made by any method :