Golfer’s Elbow
Golfer’s elbow (also called Medial Epicondylitis) is a painful condition occurring from repeated muscle contractions in the forearm that leads to inflammation and microtears in the tendons that attach to the medial epicondyle. The medial epicondyle is the bony prominence that is felt on the inside of the elbow.
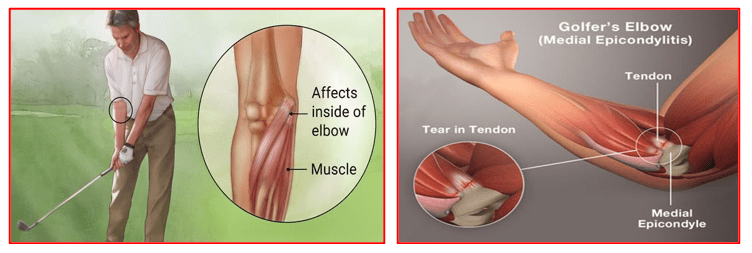
Golfer’s elbow and Tennis Elbow are similar except that Golfer’s elbow occurs on the inside of the elbow and Tennis Elbow occurs on the outside of the elbow. Both conditions are a type of Tendonitis which literally means – inflammation of the tendons.
Golfer’s Elbow is usually caused by overuse of the forearm muscles and tendons that control wrist and finger movement but may also be caused by direct trauma such as a fall, car accident, or work injury.
Golfer’s elbow is commonly seen in golfers, hence the name, especially when poor technique or unsuitable equipment is used when hitting the ball. Other common causes include any activity that requires repetitive motion of the forearm such as: painting, hammering, typing, raking, pitching sports, gardening, shovelling, fencing, and playing golf.
The symptoms of Golfer’s Elbow can include the following:
- Elbow pain that appears suddenly or gradually
- Achy pain to the inner side of the elbow during activity
- Elbow stiffness with decreased range of motion
- Pain may radiate to the inner forearm, hand or wrist
- Weakened grip and difficulty in holding objects.
- Pain worsens with gripping objects
Golfer’s diagnosis is based on patient’s history and clinical examination.
Patients have typical symptoms as above. They have tenderness on probing the inner side of the elbow. There may be localised swelling on the inner side and limited elbow motion. Patient’s elbow pain is exacerbated when the wrist is flexed or bent forward toward the forearm
Surgeon may order an x-ray to rule out a fracture or arthritis as the cause of elbow pain.
Occasionally, if the diagnosis is unclear, the surgeon may order further tests to confirm golfer’s elbow such as MRI or ultrasonography of the affected elbow.
The treatment options available for treating golfer’s elbow are non-surgical (conservative) and surgical.
All patients are first recommended conservative treatment options to treat the golfer’s elbow symptoms. These may include:
- Activity Restrictions: Limit use and rest the arm from activities that worsen symptoms
- Orthotics: Splints or braces may be ordered to decrease stress on the injured tissues
- Ice: Ice packs applied to the injury will help diminish swelling and pain. Ice should be applied over a towel to the affected area for 20 minutes four times a day for a couple days. Never place ice directly over the skin
- Medications: Anti-inflammatory medications are prescribed to treat the pain and swelling
- Physiotherapy: is ordered for strengthening and stretching exercises to the forearm once patient’s symptoms have decreased
- Pulsed Ultrasound: A non-invasive treatment used by physiotherapists to break up scar tissue and increase blood flow to the injured tendons to promote healing
- Professional golfing instructions: Consulting with a sports professional to assess and instruct in proper swing technique and appropriate equipment may be recommended to prevent recurrence
- Injections: In cases failing to respond to above measure by 6 to 12 weeks, surgeons can give a steroid injection into the painful. This helps reduce inflammation, pain and swelling. Though these are cheaper, some patients develop hypo-pigmented (white) patches at the injection site that may take 4 to 6 months to settle down. This creates unwanted patient anxiety during treatment.
- Platelet rich plasma (PRP) injections are now popular and widely used. They have growth factors that assist in healing of the inflamed tendon.
Surgery:
If conservative treatment options fail to resolve the condition and symptoms persist for 6 to 12 months, your surgeon may recommend surgery to treat Golfer’s Elbow. The goal of surgery to treat Golfers Elbow is to remove the diseased tissue around the inner elbow, improve blood supply to the area to promote healing, and alleviate the patient’s symptoms.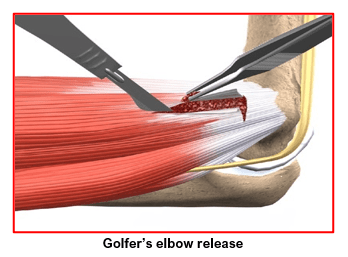
After surgery, patients are given anti-inflammatory painkillers and asked to do daily ice-packing for 4 to 5 times. They are also sent for elbow physiotherapy which is performed as tolerated. This helps in improving the elbow range of motion, muscle strength and function.
Book An Appointment
Private Clinics : Locations & Directions
London Joints Clinic (Pune)
Address
Office S 5, 2nd Floor, North Block, Sacred World Mall,
Opp Sacred Heart Township, Near Jagtap Chowk,
Wanawadi, Pune 411040
Monday to Saturday
6 PM to 9 PM
Appointments
Hospitals OPDs : Locations & Directions
Jupiter Hospital (Baner)

Address
Lane 3, Baner- Balewadi Road,
Prathamesh Park,
Baner, Pune 411 045
Monday to Saturday 11 AM to 4 PM
Appointments
Contact us
Dr Anand Jadhav has a centralised appointment system for all locations across various hospitals and clinics in Pune & PCMC areas
Appointment Bookings & Requests can be made by any method :