Frozen Shoulder
(Adhesive Capsulitis)
Adhesive Capsulitis, more commonly known as ‘Frozen Shoulder’, is a condition causing pain and stiffness within the shoulder joint. It is reported to affect approximately 2% of the general population.
The lining of the shoulder joint, known as the 'capsule', is normally a very flexible elastic structure. It's looseness and elasticity allow the shoulder to have a wide range of motion.
Adhesive capsulitis occurs when the soft tissues of the shoulder joint begin to get inflamed, thickened and contracted from scar tissue formation. This loss of normal tissue elasticity and the development of adhesions within the joint capsule, causes pain and stiffness in the shoulder.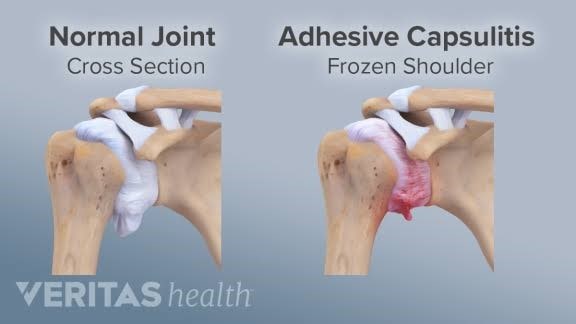
The cause of adhesive capsulitis (frozen shoulder) is not fully understood. There is no clear connection to arm dominance, occupation or athletic activity.
Frozen shoulder can be of two types – Primary or Secondary
Primary (Idiopathic) frozen shoulder is a distinct pathological condition identified by global limitation of shoulder motion, with a loss of compliance of the shoulder capsule, with no specific underlying cause found.
Secondary frozen shoulder typically presents after surgery, injury, or prolonged immobilisation. It may also follow an accompanying condition, such as subacromial impingement or a rotator cuff tear.
Frozen shoulder has been found to be more common in association with the following conditions:
- Diabetes (10-20% association) - There is a 2-4 times increased risk for diabetics of developing frozen shoulder. Insulin-dependent diabetics have a 36% chance of developing it, 10% bilaterally and the condition tends to be more severe in diabetics.
- Cardiac problems
- Lipid problems – raised cholesterol levels
- Endocrine abnormalities, particularly hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism.
- Trauma
- Surgery in the shoulder, neck or breast region
Frozen shoulder develops and progresses through the following 3 stages:
Each stage can last for 6 months (range of 3 to 9 months)
Freezing- During the freezing stage, the patient starts developing slow onset pain that steadily worsens. With increasing pain, the shoulder joint also starts stiffening up.
Frozen- During the frozen stage, the shoulder pain typically starts reducing but the joint stiffness remains. Daily living activities become quite difficult during this stage.
Thawing- During the thawing stage, shoulder motion returns and pain subsides.
Patients with adhesive capsulitis can be troubled for 6 months to 2 years as they pass through the different stages of the disease. The final recovery of motion may be incomplete in some patients.
The most common symptoms of frozen shoulder are chronic pain, joint weakness and loss of motion from extreme stiffness.
- The pain is often reported by patients as a constant aching or dull pain located over the outer portion of the shoulder. Certain patients may also experience pain in the upper arm. Pain gets worse with forceful movements.
- Patients are not able to sleep on the affected side due to pain. Some patients get disturbed from their sleep due to onset of pain after sleeping.
- The accompanying stiffness makes it difficult for patients to perform activities of daily living like changing clothes, reaching round the back, combing hair or lifting arm into overhead positions.
- There may be weakness of the rotator cuff tendons due to tendinitis or tears
The diagnosis of frozen shoulder is made on the basis of medical history, clinical examination and appropriate investigations.
- A through medical history is taken. Patients may give history of diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, trauma etc. Frozen shoulder is more common in females than males. It generally affects patients in their mid-forties or mid-fifties.
- Both Shoulder joints are carefully examined for tender areas, range of motion, any limitation of mobility, strength of the rotator cuff tendons and the status of nerves and blood vessels.
- The cervical spine is also examined as a routine.
- All findings are carefully documented so as to allow comparison of clinical findings during subsequent follow-up visits.
Investigations in Frozen Shoulder:
X-rays of shoulder – may be normal or they may show signs of subacromial impingement.
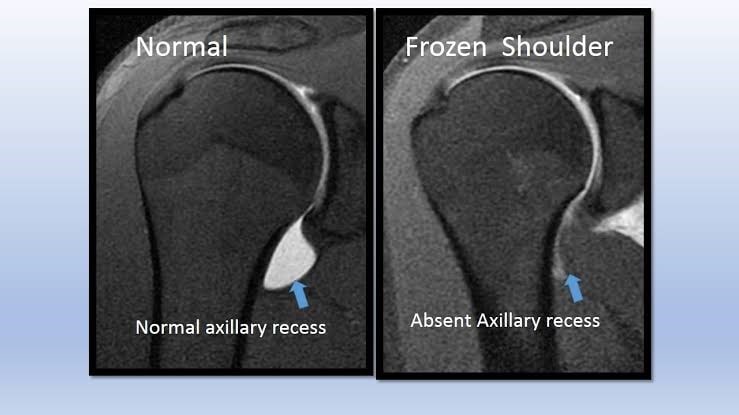
MRI of shoulder – will show inflamed & contracted capsule especially in the lower region (axillary pouch) and the rotator interval (area between two tendons). The scan can also show swollen bursae, inflamed or torn rotator cuff tendons, swollen tendon of the long head of biceps, presence of any pinching bony spurs etc.
Most patients with frozen shoulder will improve significantly over a period of 1 to 2 years after the onset of symptoms. But increasing pain and limited mobility due to the stiff shoulder generally require treatment.
The type of treatment provided depends on the severity of the pain, amount of stiffness and the stage of patient’s disease process.
Conservative (Non-Surgical) Treatments
Frozen shoulder treatment most often begins with non-operative measures to help control pain, regain shoulder range of motion and improve overall function.
Conservative (Non-Surgical) treatment includes:
- Rest from work & activity modifications
- Warm or cold fomentation followed by application of analgesic gels
- Pain killer & anti-inflammatory medications are prescribed as needed
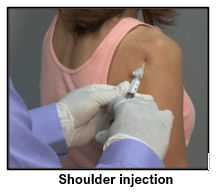
- Intra-articular steroid injections – helps in reducing joint inflammation and pain
- Physiotherapy - started after first controlling pain with medications and rest. It helps to prevent any further stiffness, regain range of shoulder motion and also strengthens the rotator cuff muscles.
Surgical Treatment for Frozen Shoulder:
Dr Jadhav recommends an arthroscopic surgical procedure if the frozen shoulder symptoms do not settle down over a period of 3 to 6 months. It is also recommended if the patients are unable to cope with their symptoms.
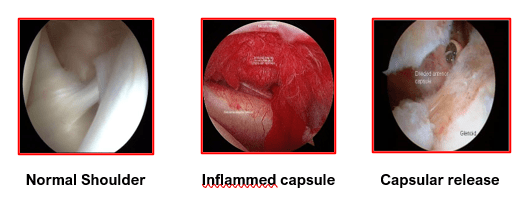
This procedure is called Arthroscopic Capsular Release. It involves controlled release or cutting of thickened and contracted capsular tissues with specialised radio-frequency devices.
Such controlled release under vision avoids the risks that are associated with a blindly performed shoulder manipulation under anaesthesia (MUA) like tear of the rotator cuff, damage to the articular surfaces or fractures of the upper humerus. These radio-frequency devices also help in removing inflamed synovial tissue as well as sealing any bleeding points after release or cutting of scarred tissues.
The operating surgeon can immediately see the real improvement in the range of shoulder movements on the operating table. Videos of the patient’s shoulder range of motion are recorded, both before and after the surgery. These videos are then shared with the patient in order to motivate them to do their exercises after surgery.
Intensive physiotherapy is essential after this surgery.
Arthroscopic Capsular Release is excellent for pain relief and restoring shoulder movements, with a success rate of more than 90% at 6 months.
Early surgery has been shown to be of significant benefit for faster pain relief, quicker recovery of function and earlier return to work.
Performing surgery early in the disease process is like removing a patient from a ‘bad cycle’ of pain, stiffness and compromised quality of life.
Book An Appointment
Private Clinics : Locations & Directions
London Joints Clinic (Pune)
Address
Office S 5, 2nd Floor, North Block, Sacred World Mall,
Opp Sacred Heart Township, Near Jagtap Chowk,
Wanawadi, Pune 411040
Monday, Wednesday & Friday 7 PM to 9 PM
Sunday 11 AM to 1 PM
Appointments
London Joints Clinic ( PCMC )
Address
C/O Dr Nitin’s Physio Clinic,
Opp. Brahma Hotel,
Near Akurdi Post Office,
Vivek Nagar,
Akurdi,
Pune 411035
Saturdays only 4.30 PM to 7.30 PM
Appointments
Hospitals OPDs : Locations & Directions
Manipal Hospital

Address
Manipal Hospital, Opp D Mart, Baner-Mhalunge Road, Baner, Pune 411 045
Monday to Saturday 11 AM to 4 PM
Appointments
Contact us
Dr Anand Jadhav has a centralised appointment system for all locations across various hospitals and clinics in Pune & PCMC areas
Appointment Bookings & Requests can be made by any method :