De Quervain’s
Tenosynovitis
De Quervain’s tenosynovitis is a condition brought on by irritation or inflammation of the wrist tendons at the base of the thumb.
This condition has been named after the Swiss surgeon Fritz de Quervain. It is also known as First dorsal compartment tendonitis tenosynovitis.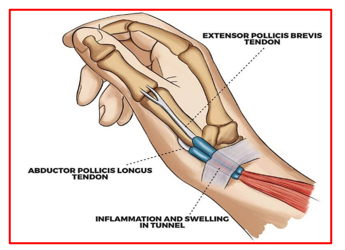
The inflammation causes the compartment (a tunnel or a sheath) around the tendon to swell and enlarge, making thumb and wrist movement painful. Making a fist, grasping or holding objects—often infants—are common painful movements with de Quervain’s tenosynovitis.
The cause of de Quervain’s tenosynovitis is an irritation of the tendons at the base of the thumb. This commonly arises due to:
- Repetitive activities and overuse of the thumb.
- Nursing mothers holding the babies in an awkward position plus hormonal changes in the body. Both these reasons put strain on the thumb tendons.
- Grandmothers holding babies in an awkward position.
- Wrist fractures can also predispose a patient to De Quervain’s tenosynovitis, because of increased stresses and friction across the tendons during wrist and thumb movements.
The diagnosis of De Quervain’s tenosynovitis is based on typical patient symptoms and clinical examination of wrist and thumb.
Patients symptoms may be:
- Pain over the thumb-side of the wrist is the main symptom. The pain may appear either gradually or suddenly. It is located at the first dorsal compartment at the wrist. Pain may radiate down the thumb or up the forearm.
- Difficulty in moving their thumb
- Sense of catching or snapping when moving the thumb
- Difficulty with holding objects like glass of water or teacup
- Pain and difficulty when holding a pen or during pinching type activities of the thumb
- Swelling over the base of thumb area and lower wrist
- Irritation of the nerve lying on top of the tendon sheath may cause numbness on the back of the thumb and index finger
Patients may have swelling and tenderness over the thumb side of lower wrist. Bending the wrist towards the little finger, with fingers clasped over the thumb, is very painful.
X-rays of the wrist may be needed in some patients to see for bony projections secondary to old fractures or tissue calcifications.
Treatment for De Quervain’s tenosynovitis can be conservative or surgical.
Conservative measures are helpful in the majority of patients:
- Lifestyle changes – avoid repeated use of affected hand, more use of unaffected hand for work, avoid holding or carrying heavy objects in affected hand
- Anti-inflammatory painkiller medications are taken to control pain and reduce inflammation. Additionally, nerve supplements and pain modifying oral medications are also prescribed for 2 to 4 weeks.
- Use of a thumb spica splint prevents bending of the wrist and thumb. This avoids irritation of the thumb tendon and helps to reduce pain. This may be used during work only or regularly including night times depending on the severity of symptoms. Splinting at night helps prevent night pain and improves patient’s sleep.
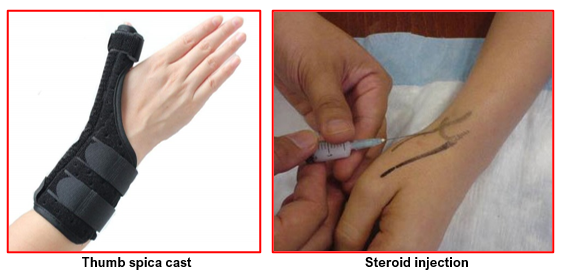
- Steroid injection in the first extensor compartment helps reduce inflammation around the tendons. This reduces pain and swelling. But this injection can cause white patch skin discolouration temporarily at the injection site. This can cause unnecessary patient anxiety and hence they need to be forewarned about this possibility. There is also a small risk of rupture of the thumb extensor tendon due to tendon weakening and affection of its blood supply.
- Platelet rich plasma (PRP) injection is obtained from patient’s own blood. It delivers readymade growth factors derived from the patient’s platelets. This assists in healing of the tendon lesion and reduces patient’s pain and swelling. But this injection is expensive compared to a steroid injection.
Surgery: is rarely required. Needed for patients not responding to conservative measures.
It is done under local anaesthesia as a day care surgery.
The first dorsal compartment sheath of the extensor tendons is exposed and opened up surgically. The tendons are confirmed to be moving freely without any friction. The wound is then closed with absorbable sutures and sterile dressing bandage is applied.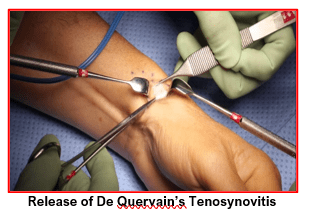
Surgery gives pain relief and the swelling gradually settles down. It creates more room for frictionless motion of the thumb tendons and avoids future flare ups of same problem. It can take 6 to 8 weeks for resumption of all normal activities.
The risks associated with De Quervain’s release are:
- Infection
- Swelling
- Stiffness
- Bleeding
- Bruising
- Scar tenderness
- Damage to sensory branch of radial nerve leading to numbess or formation of a painful neuroma
Book An Appointment
Private Clinics : Locations & Directions
London Joints Clinic (Pune)
Address
Office S 5, 2nd Floor, North Block, Sacred World Mall,
Opp Sacred Heart Township, Near Jagtap Chowk,
Wanawadi, Pune 411040
Monday to Saturday
6 PM to 9 PM
Appointments
Hospitals OPDs : Locations & Directions
Jupiter Hospital (Baner)

Address
Lane 3, Baner- Balewadi Road,
Prathamesh Park,
Baner, Pune 411 045
Monday to Saturday 11 AM to 4 PM
Appointments
Contact us
Dr Anand Jadhav has a centralised appointment system for all locations across various hospitals and clinics in Pune & PCMC areas
Appointment Bookings & Requests can be made by any method :