Ankle Arthroscopy
Ankle arthroscopy is a commonly performed minimally invasive or key-hole surgery of the ankle. The surgeon first makes portals (tiny keyholes) at pre-marked safe zones around the ankle. He then inserts an arthroscope (small telescope) with attached video camera to look into the ankle joint from one portal and special instruments, as needed, are used through the other portals.
The images from inside the ankle are seen on a large screen monitor which helps the surgeon to diagnose or treat multiple ankle problems under arthroscopic vision. Images of the ankle pathologies and videos of the surgery can also be recorded. Patients are given a copy of these photos and video recordings.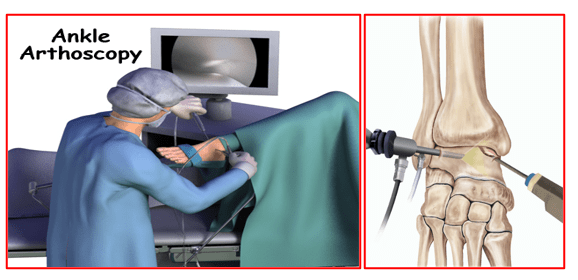
Ankle arthroscopy is a relatively safe procedure and a majority of the patients get discharged from the hospital on the same day of surgery or the next day.
Dr Anand Jadhav has 25 years of surgical experience. He has undergone highly advanced and specialised training in arthroscopic surgeries of the ankle joint across multiple centres in the UK, Europe and the USA. He prefers to do ankle arthroscopic surgeries at hospitals that have all the necessary specialised equipment along with trained support staff. This helps him in providing best outcomes to his patients.
Ankle arthroscopy, being a minimally invasive procedure, offers several advantages:
- Smaller scars which are cosmetically better
- Less tissue injury
- Minimal pain
- Shorter hospitalisation (day care or 1 day stay)
- Faster recovery
- Lower infection rates
The ankle joint is vulnerable to a variety of injuries as well as non-traumatic lesions.
The most common ankle problems where ankle arthroscopy may be recommended for diagnosis and treatment are:
- Debridement of loose bodies such as bone chips or torn cartilage tissue
- Removal of scar tissue and release of ankle joint contractures
- Removal of bony spurs: These are extra bony growths, at the ends of the bones, caused by injury or arthritis. These cause pain and limit ankle mobility. e.g. Footballer’s ankle in the front or os trigonum at the back of the ankle
- Removal of synovial tissue (synovectomy) in rheumatoid arthritis
- Management of osteochondral lesions of the body of talus.
- Arthroscopic fusion of the ankle joint
- Soft tissue biopsy from the ankle joint
- Arthroscopic joint debridement for managing ankle joint infections
- Arthroscopic assisted ankle fracture fixation
- Ankle arthroscopy is commonly performed under general anaesthesia or spinal anaesthesia as a day-care or 1 day stay procedure in a suitably counselled and consented patient.
- The patient is placed in a supine or prone position depending on his ankle pathology that needs to be dealt with. This allows the surgeon to easily adjust the arthroscope and have a clear view of the inside of the ankle compartments. Mechanical distraction devices are sometimes used to help surgeons temporarily enlarge the potential space of the ankle.
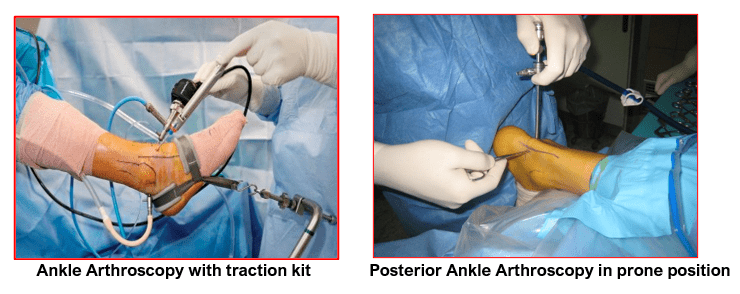
- Several tiny incisions are made at safe sites around the ankle. The first incision is made on the outer side of the ankle from the safest site. The arthroscope attached to a camera is then inserted from this lateral wound to look into the ankle joint.
- To enhance the clarity of the ankle structures through the arthroscope, the surgeon fills the ankle joint with a sterile liquid, generally normal saline. The liquid flows through the arthroscope to maintain clarity and to restrict any bleeding.
- The arthroscope with its attached camera displays the internal structures of the ankle on the video monitor and helps the surgeon to evaluate the joint and assess any pathology that is found.
- Additional portals are made and surgical instruments like probes, shaver, punches and scissors are inserted to fix the problem.
- At the end of the procedure, the surgical incisions are closed by sutures, and sterile dressings are applied. Then a soft compression bandage is applied. Surgeon may use an ankle range of motion splint, if needed, to protect any reconstructive work done on the ankle.
Ankle arthroscopy is contraindicated in patients with soft tissue infections of the ankle such as cellulitis, acute and chronic open wounds, and dermatitis overlying the ankle region. Patients with advanced and severe arthritic changes with complete loss of the joint space are not good candidates for arthroscopic debridement procedures. Patients with severe peripheral vascular disease, peripheral neuropathy, reflex sympathetic dystrophy/complex regional pain syndrome, and oedema may not be eligible for ankle arthroscopy. Dr Jadhav will thoroughly discuss with you your individual risks, potential benefits, and the alternatives to ankle arthroscopy.
- Most patients are discharged the same day or the next day after ankle arthroscopy. Recovery after the surgery depends on the type of procedure performed. Recovery from simple procedures is often fast. However, recovery from complicated or complex procedures takes a little longer. Patients are counselled pre-operatively about their recovery time which can be between 2 to 6 weeks for simple procedures and 6 to 12 weeks for complex procedures.
- Recovery from ankle arthroscopy is much faster than that from an open ankle surgery.
- Pain medicines are prescribed to manage pain for the first 3 to 5 days. Thereafter they are taken only if required.
- Ice packs are given 4 to 5 times a day and carried on for 3 to 4 weeks.
- The operated leg is kept elevated over pillows to keep it above the level of the heart. This reduces pain and swelling.
- Physiotherapist visits patients prior to their discharge from the hospital. Ankle exercises are taught and then carried on by patient at home for minimum of 4 to 6 weeks. Weight bearing is allowed as per the type of ankle procedure performed. Patients need to use a pair of walking crutches for 2 to 4 weeks. For complex surgeries patients may need to be seen by a physiotherapist on a regular basis and for longer duration of about 2 to 3 months. This type of formal rehabilitation program ensures successful and faster recovery.
- Eating a healthy diet and not smoking helps in wound healing.
The wounds get inspected and sutures are removed after 10-12 days
Ankle arthroscopy is a safe procedure and complications are very rare.
Complications that may arise from ankle arthroscopic surgery are bleeding into the ankle joint, infection, swelling, ankle stiffness, blood clots, damage to surrounding nerves, blood vessels, joint cartilage, ligaments and continuing ankle problems.
Book An Appointment
Private Clinics : Locations & Directions
London Joints Clinic (Pune)
Address
Office S 5, 2nd Floor, North Block, Sacred World Mall,
Opp Sacred Heart Township, Near Jagtap Chowk,
Wanawadi, Pune 411040
Monday to Saturday
6 PM to 9 PM
Appointments
Hospitals OPDs : Locations & Directions
Jupiter Hospital (Baner)

Address
Lane 3, Baner- Balewadi Road,
Prathamesh Park,
Baner, Pune 411 045
Monday to Saturday 11 AM to 4 PM
Appointments
Contact us
Dr Anand Jadhav has a centralised appointment system for all locations across various hospitals and clinics in Pune & PCMC areas
Appointment Bookings & Requests can be made by any method :