Ankle Arthritis, Fusion
& Ankle Joint Replacement
Ankle arthritis is a condition wherein the smooth cartilage lining the articulating surfaces of the ankle joint gets worn out. This leads to rubbing of the worn surfaces, pain, swelling and limitation of ankle movements.
Even though ankle arthritis is less prevalent than arthritis affecting the knee and hip, it can be equally debilitating and painful.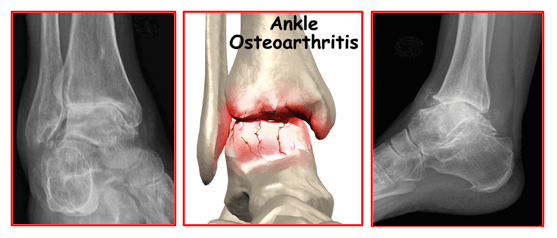
Ankle Arthritis is commonly caused due to:
Osteo-arthritis – age related wear and tear of the articular cartilage
Rheumatoid arthritis – autoimmune inflammatory disease disorder
Post-traumatic arthritis - secondary to articular fractures, malunited fractures around the ankle, ankle dislocations or chronic instability
Post-infective ankle arthritis.
Patients with ankle arthritis may complaint of:
- Pain on moving the ankle joint.
- Ankle stiffness, especially in the morning or at start of any activity
- Swelling and deformity of the ankle joint
- Difficulty in walking or weight bearing on the affected leg
- Limp on walking
Grating or locking sensation in the ankle
Ankle arthritis is diagnosed based on patient’s typical symptoms, his medical history, thorough clinical examination and x-rays of the ankle joint.
CT scans and MRI scans of the ankle are not routinely needed for diagnosis. Blood tests may be needed for confirming inflammatory arthritis.
Ankle arthritis can be treated based on patient’s symptoms, stage of his ankle arthritis and functional difficulties.
The treatment may be conservative or surgical.
All patients are given conservative treatment in the initial stages.
This involves:
Activity modifications – patients are educated about their disease and taught lifestyle modifications to reduce their pain and keep it under control. Pain inducing activities like running, jumping, prolonged standing or walking are avoided. Patients can learn to lead an active lifestyle with some minor changes to their routine activities. They are also advised to lose weight.
Anti-inflammatory and Pain-killer medications – these help in controlling pain and reducing inflammation. This results in improved mobility. There are various types of medications available for pain control. These medications are prescribed taking into account the patient’s pain intensity, health profile and his safety. All such medications must be taken as per doctor’s advice and instructions.
Physiotherapy. A physiotherapist may perform ultrasound and other techniques to decrease inflammation. Regular ankle exercises help in improving ankle mobility and pain reduction. Walking support in the form of a stick, crutch or walker may be needed for support and off-loading the ankle joint. Physiotherapist trains patients to help mobilise safely using any support.
Chondro-protective agents – Glucosamine and chondroitin sulphate are considered as chondro-protective medications. These slow down the process of arthritis and thought to help in regrowth of the cartilage. This helps in pain relief. These medications need to be taken together in appropriate doses for best possible result.
Customised foot orthotics. A custom foot orthotic is a doctor prescribed arch support that is made directly from a casting (mold) of your feet, and theoretically should provide superior support compared to shoe insert that you would purchase from a pharmacy. In the case of ankle arthritis with a flat foot, the orthotic may be able to improve the position and alleviate discomfort.
Custom ankle foot orthotic. A combined custom foot and ankle brace can support the foot and limit painful motion of the ankle. This reduces pain and improves mobility.
Visco-supplementation – This involves injecting the ankle joint with special liquids (hyaluronic acid) that increase the viscosity of the joint fluid and improve the health of the ankle cartilage. This leads to improved joint lubrication and reduced friction between the arthritic surfaces of the ankle joint. Minor cartilage lesions are thought to heal with such injections. Their pain-relieving effect lasts for 6 months to 12 months. Ideally most useful for early stages (mild to moderate) ankle arthritis in young patients. Based on their viscosity these injections can be a single dose or multiple dose therapy.
Corticosteroid injection. An intra-articular cortisone injection is a powerful anti-inflammatory medication that is used to rapidly reduce the pain associated with an arthritic joint, especially due to rheumatoid arthritis or osteo-arthritis. The pain relief that may be experienced from the injection is often temporary lasting for 2 to 3 months. Multiple injections must be avoided for the risk of infection in the ankle joint.
PRP injection. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is a concentration of growth factors derived from patient’s own blood. It can be injected directly into the arthritic joint. The PRP is thought to stimulate stem cells to decrease inflammation and symptoms.
Surgical treatment:
These options are offered to patients not responding to conservative treatment or in whom it has stopped giving lasting relief.
Surgery for arthritis of the ankle varies depending on the location of arthritis, severity of arthritis, malalignment, and the presence of structural foot deformity (i.e., flat feet).
These procedures are generally separated in two kinds: Joint sparring (preserves the joints) or Joint destructive that eliminates the ankle joint through fusion or replacement.
Joint Preserving Procedure:
Arthroscopic Ankle Debridement is a joint preserving procedure that involves “surgical cleaning” of the arthritic components of the joint to alleviate pain, increase ankle motion and improve function.
This keyhole technique is best indicated for mild to moderate ankle arthritis. The benefit of this joint preserving procedure is that it does not burn any bridges and if it does not resolve patient’s symptoms to a satisfactory level, then more advanced procedures can be advised.
Arthroscopic Ankle Debridement: Ankle arthroscopy is performed through tiny incisions (portals) that are strategically placed around the ankle joint. Arthroscopy helps in clearly seeing all compartments of the ankle joint. Loose free fragments of cartilage, flaps of cartilage, loose bodies, thickened synovial tissue and any other joint debris get cleaned up using specialised instruments. Scar tissue gets excised, arthritic bony spurs (osteophytes) gets removed from around the ankle joint bones and any bony cysts too get evacuated with a shaver. Micro-fracture technique can also be used for allowing small cartilage defect areas to be covered with fibrous cartilage.
At the end, the ankle joint is thoroughly washed off all debris and the wounds are sutured or taped. Sterile compression bandage is applied over the wound dressings.
Effectiveness of all above steps depends on the extent of the ankle arthritis. The recovery after ankle arthroscopy is fairly quick, and patients are frequently mobilising immediately after the procedure, depending on the extent of the debridement.
Joint Destructive Procedures:
Ankle Joint Fusion and Ankle Joint Replacement are the 2 solutions for end stage arthritis affecting the ankle joint. End stage arthritis is when there is significant loss of the joint cartilage with exposure of the underlying bones, arthritic bony spurs, bony cysts and deformed articulating bones.
Ankle Fusion (Ankle Arthrodesis) is a joint destructive procedure that involves permanently locking the arthritic ankle joint in place. It is the gold standard and time-tested procedure for end stage ankle arthritis. An ankle fusion is considered as a life-long solution for ankle arthritis.
The ends of the bones articulating with each other at the ankle are jammed permanently to allow bony healing by formation of bony bridges across the ankle joint bones forming one mass. It is ideally suited for younger patients who are involved with heavy physical work and also for severely deformed and mal-aligned ankle joints.
This surgery can be done arthroscopically or by open technique.
Arthroscopic ankle fusion is used for ankles with advanced arthritis and reasonable ankle joint alignment. But for arthritic ankles with severe bony deformities and ankle joint mal-alignment, open surgery is more suitable.
Ankle fusion helps to:
- correct structural abnormalities at the ankle joint
- reduce pain & improve the ability of patients to weight bear and mobilise without pain
- improve ankle & foot cosmetic appearance
- improve patient’s functional abilities & quality of life
Most people who require ankle fusion, have already experienced many years of ankle stiffness with limited motion and have already compensated their gait and walking patterns. Hence ankle fusion does not typically affect patient’s walking adversely.
Even though ankle motion is eliminated by ankle fusion surgery, the adjacent joints compensate and may allow up to 50% of this motion to return. But in the long term, degenerative arthritis does occur in these adjacent joints. About 5 to 10% of patients will require fusion of other joints at some stage in the future.
During open ankle fusion surgery, surgeon makes an incision at the front of the ankle joint. The joint is exposed by moving aside the soft tissues in the front. Then the arthritic surfaces of the distal tibia and the upper talus are cleared off their remaining articular cartilage to expose the raw bones underneath. The ankle joint structural deformity is then corrected. The ankle joint is held in a stable and functionally neutral position. Reduction is confirmed under an image intensifier x-ray machine. Temporary wires are now passed across the ankle joint, to hold the exposed bones in the correct position.
Finally, fixation implants are used to permanently hold the articulating bones in a stable and compressed position. This definitive fixation is achieved either with the help of 2 to 3 special screws or a plate and screws together. Final x-rays are taken, and the wounds are closed with staples or sutures. Sterile dressings are applied. Patients are given a temporary plaster back-slab for support.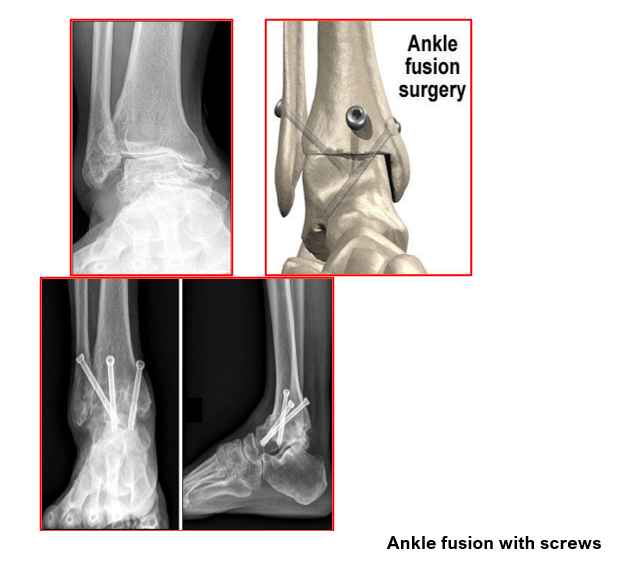
Arthroscopic ankle fusion follows the same principles, like the open surgery and gets done via tiny scars around the ankle joint. It offers the advantage of less pain, less tissue damage, less swelling, faster healing of the tiny wounds, better cosmesis, and faster recovery.
The patient’s progress after ankle fusion surgery is as follows:
- Hospital stay is typically for 1 -2 days.
- From the next day of surgery, patients are mobilised non-weightbearing (NWB) with help of elbow crutches or a walker. They need to remain NWB for a minimum of 6 weeks.
- They are prescribed simple painkillers like paracetamol on discharge and advised to keep their leg elevated when resting for the next 3 to 4 months. This helps in reducing their pain and swelling.
- Icepacks are applied to the front of the back-slab for 4 to 5 times a day
- Patients are encouraged to do toe movements, static quadriceps exercises and breathing exercises.
- Patients are also started on daily injections of teriparatide (parathyroid hormone) to promote bone healing. These daily injections are taken by patients themselves after being trained in the injection techniques.
- At 2 weeks the ankle wounds are checked. Sutures are removed and a below knee lightweight synthetic plaster cast is applied. This plaster cast stays on for another 4 weeks. Patients are advised to remain non-weightbearing for the first 6 weeks and use crutches or walker for support.
- At 6 weeks their plaster is removed, and check x-rays of the ankle are done to assess healing of their fusion. They are then given an ankle walker boot. Partial weight-bearing is advised depending upon the healing status on the x-rays. Operated leg elevation and toe exercises are continued. Icepacks are also used 4 to 5 times daily by taking the ankle walker boot off for short durations. Further follow-up is scheduled after 6 weeks.
- At 3 months mark, the ankle fusion is generally sound and well healed. Patients can be left free without their ankle walker and allowed to mobilise full weight bearing as tolerated. But they are instructed to carry on using a walking support until they feel comfortable and confident with their unaided walking.
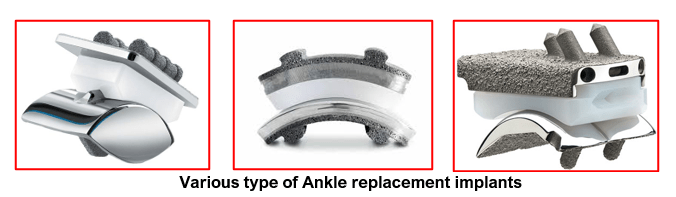
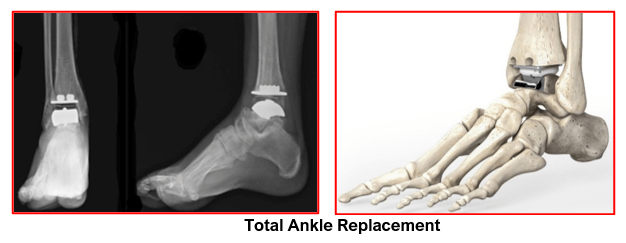
Ankle Joint Replacement
Ankle Joint Replacement is a surgical procedure in which the worn-out joint surfaces of the ankle joint are replaced with prosthetic implants.
This surgery is performed for patients having:
- Advanced stage ankle arthritis and who are not responding to conservative treatments.
- Patients having rheumatoid arthritis with advanced stage ankle arthritis
- History of previous ankle surgery and deformity (post-traumatic arthritis)
- Tumour around ankle joint
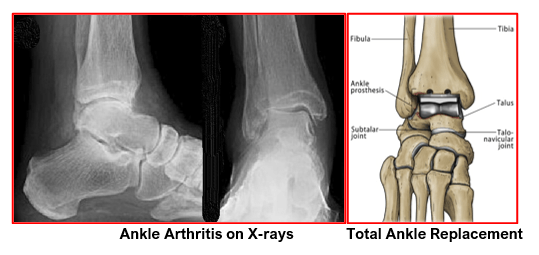
Ankle Joint Replacement can relieve pain and maintain motion in the arthritic ankle joint and is an alternative to arthrodesis (ankle fusion) which can relieve pain but eliminates motion in the joint.
It is best suited for more elderly patients (over 65) with lower demands (not heavy manual workers) and those having a well aligned ankle.
The goal of ankle joint replacement surgery is to eliminate pain and increase the mobility of the ankle joint. This surgery is performed under sterile conditions in an operating room under general or regional anaesthesia and involves the following steps:
- An incision is made over the front of the ankle joint.
- The tendons crossing the ankle joint in the front are moved away to expose the ankle joint. Care is taken to protect and safely move aside the blood vessels and nerves from the surgical site
- The damaged joint surfaces of the lower tibia and the dome of the talus are cut off with a surgical saw to create a smooth conforming surface to receive the prosthetic implants. Generally, only the tibial and talar implants are used for ankle replacement.
- Special instruments are used to prepare the lower tibia bone to insert the tibial component of the prosthesis.
Once a proper fit is established, the surgeon repeats this procedure on the talus bone to prepare it for the talar component of the prosthesis.
- The bone preparation techniques remain same in principles but may be slightly different based on the type of implant to be used.
- The lower tibia and talus bones are then prepared with or without cement, depending on the patient’s bone strength and surgeon’s preference. In elderly patients with osteoporotic bones, there is need for bone cement and cemented implants. In younger patients and those with strong bones, the surgeon uses specially coated uncemented implants.
- The metal components are inserted into the tibia and the ankle and then a high-grade plastic component is inserted between them. The assembly is now put together ensuring proper movement and stability at the ankle joint
- The surgeon then irrigates the new joint with sterile saline.
- The surgeon then sutures the joint capsule together and the wound is closed after keeping a drain in place to help drain out any blood from the surgical area.
- The ankle is then covered with a sterile dressing and compression bandage is applied
- The leg is placed in an ankle walker boot.
- Patient is sent to the recovery room for observation
The patient’s expected progress after ankle replacement surgery is as follows:
- Patients can start eating and drinking after 3-4 hours
- Regular icepacks are used 4 to 5 times a day
- Pillows are used to keep ankle elevated and above level of heart. This helps in reducing pain and swelling
- Intravenous antibiotics are given for first 24 hours only.
- The suction drain gets removed after 24 hours & wound dressings are changed.
- Physiotherapy is started soon after surgery. It is continued for 3 months to help regain full ankle range of motion.
- Patient stays in the hospital for 2 to 3 days after the surgery.
- Wound gets inspected and the sutures are removed at 12 to 14 days post-surgery.
- Patients are instructed to keep the wound dry. Bathing and showering are generally allowed after wound healing and suture removal around 14 days post-surgery.
- Patients are given specific instructions about do’s and don’ts and advised to carry on physiotherapy under supervision.
- They are encouraged to eat a healthy diet and stop smoking to promote healing.
Most patients suffer no complications following Ankle Joint Replacement. However, complications can occur following ankle surgery and include:
- Swelling
- Infection
- Fractures of the tibia or talus
- Dislocation of the ankle joint or ankle instability
- Malalignment of the bones
- Damage to nerves or blood vessels
- Blood clots (Deep Venous Thrombosis)
- Ankle stiffness
- Loosening of implants
- Wearing out of the components
- Wound irritation and scar tenderness
- Failure to relieve pain
Ankle joint implants can last for 10-15 years. If they loosen out and become symptomatic, then it needs implant removal and conversion to ankle fusion
Book An Appointment
Private Clinics : Locations & Directions
London Joints Clinic (Pune)
Address
Office S 5, 2nd Floor, North Block, Sacred World Mall,
Opp Sacred Heart Township, Near Jagtap Chowk,
Wanawadi, Pune 411040
Monday, Wednesday & Friday 7 PM to 9 PM
Sunday 11 AM to 1 PM
Appointments
London Joints Clinic ( PCMC )
Address
C/O Dr Nitin’s Physio Clinic,
Opp. Brahma Hotel,
Near Akurdi Post Office,
Vivek Nagar,
Akurdi,
Pune 411035
Saturdays only 4.30 PM to 7.30 PM
Appointments
Hospitals OPDs : Locations & Directions
Manipal Hospital

Address
Manipal Hospital, Opp D Mart, Baner-Mhalunge Road, Baner, Pune 411 045
Monday to Saturday 11 AM to 4 PM
Appointments
Contact us
Dr Anand Jadhav has a centralised appointment system for all locations across various hospitals and clinics in Pune & PCMC areas
Appointment Bookings & Requests can be made by any method :