Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition caused by pinching of the median nerve at the wrist leading to numbness, tingling, pain or weakness in the patient’s hand.
Carpal tunnel is a space at the wrist where the median nerve and 9 tendons pass from the forearm into the hand under the flexor retinaculum (transverse carpal ligament) that forms its roof.
When there is increased pressure within the carpal tunnel, the median nerve gets compressed against the flexor retinaculum. This causes the nerve to swell up and its function gets affected. This leads to the typical symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome.
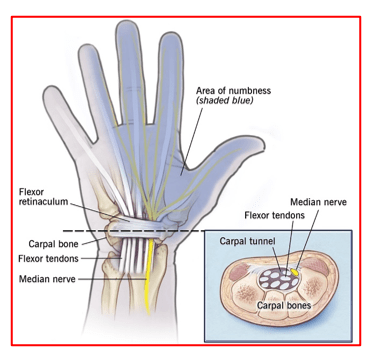
Carpal tunnel syndrome happens due to increased pressure within the carpal tunnel. It is more common in women than men, patients having small carpal tunnels within their family and occupations like typist, cashier, hairstylist or musician.
Carpal tunnel syndrome can arise due to multiple reasons:
- swelling of the flexor tendon lining called tenosynovitis,
- wrist joint fractures and dislocations,
- arthritis at the wrist joint,
- using wrist for prolonged periods in bent position,
- fluid retention in pregnancy etc.
- Thyroid conditions (hypothyroidism), rheumatoid arthritis, obesity and diabetes are risk factors for getting carpal tunnel syndrome.
Carpal tunnel syndrome symptoms typically include pain, numbness, tingling, weakness or a combination of these.
The numbness or tingling most often takes place in the thumb, index, middle, and ring fingers. The symptoms usually are felt during the night but also may be noticed during daily activities such as driving or reading a newspaper. Patients may sometimes notice a weaker grip, occasional clumsiness, and a tendency to drop things. In severe cases, sensation may be permanently lost and the muscles at the base of the thumb slowly shrink (thenar atrophy), causing difficulty with pinch.
The diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome is made based on typical patient history, thorough clinical examination and investigations to confirm the diagnosis.
Tapping along the course of the medial nerve causes tingling in the fingers (Tinel’s sign). There may be wasting (thinning) of the thumb muscles. Keeping the wrist in bent position for over 20 to 30 seconds brings on the typical symptoms.
Based on the typical symptoms, medical history and clinical examination findings, the investigations get advised.
Electrodiagnostic studies like nerve conduction velocities (NCV) and electromyogram (EMG) are done to confirm the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome as well as to check for other possible nerve problems. It also helps to understand the severity of nerve compression.
Wrist x-rays and blood tests may be needed for finding a cause for CTS based on patient’s history.
Treatment for carpal tunnel syndrome is conservative in majority of patients. Surgery is rarely required and is needed for patients not responding to conservative measures.
Conservative measures:
- Lifestyle changes – avoid repeated use of affected hand, use unaffected hand for work and avoid working prolonged hours at work by taking regular breaks.
- Management of any underlying medical condition helps giving relief from symptoms.
- Simple painkiller medications are taken to control pain. Additionally, nerve supplements and pain modifying oral medications are also prescribed for 4 to 6 weeks.
- Wrist & hand exercises help in stretching and strengthening. Improve nerve gliding, within the carpal tunnel and make patients feel better.
- Use of a wrist splint prevents bending of the wrist and avoids nerve irritation. This may be used during work only or regularly including night times depending on the severity of symptoms. Splinting at night helps prevent night sleep and improves patient’s sleep.
- Steroid injection in the carpal tunnel helps reduce inflammation and pressure around the nerve.
Surgery is the last resort for patients who have ongoing symptoms despite 3 to 6 months of conservative therapy or those who present with severe symptoms of CTS and severe compression of the nerve as confirmed on their nerve conduction studies.
Carpal tunnel release surgery can be done under local anaesthesia as a day care surgery through a single small scar at the front of the palm near the wrist.
It involves cutting the flexor retinaculum (transverse carpal ligament) that forms the roof of the carpal tunnel whilst taking precautions to protect the underlying median nerve. This surgery creates more room for the median nerve.
The surgeon then checks the status of the compressed nerve and confirms that the nerve is free of any compression along its course from forearm into the hand. Wound is closed with dissolving sutures and sterile sticky tapes which are left on for 12-14 days after surgery.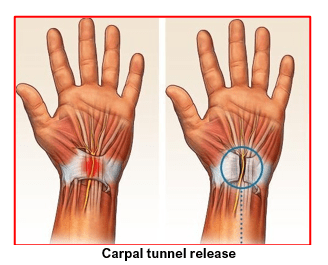
Patients notice immediate symptom relief, but full recovery can take 2 to 3 months based on the severity of the compression. All patients are forewarned that it is normal for the scar to remain tender for 3 to 4 months after surgery.
In some patients, especially the ones with severe compressions, their symptoms may not go away completely though their quality of life and hand function will be much improved.
Patients can try the following measures to avoid carpal tunnel syndrome:
- Keep wrists as straight as possible
- Use a wrist splint to keep it in a neutral position
- Avoid repeated flexion and extension movements at the wrist
- Avoid working long hours at a stretch. Take frequent breaks whenever possible
- Keep hands warm
Be mindful of posture and maintain correct position of wrists and hands at work.
The possible risks and complications associated with carpal tunnel release surgery are not very common and include:
- infection
- swelling
- bruising
- stiffness
- bleeding – if a vessel in the palm gets damaged
- scar tenderness – pain felt over the scar
- pillar pain – pain felt on either side of the scar
- numbness
- neuroma – if a small nerve gets damaged
- failure to relieve symptoms
recurrence of carpal tunnel syndrome
Book An Appointment
Private Clinics : Locations & Directions
London Joints Clinic (Pune)
Address
Office S 5, 2nd Floor, North Block, Sacred World Mall,
Opp Sacred Heart Township, Near Jagtap Chowk,
Wanawadi, Pune 411040
Monday to Saturday
6 PM to 9 PM
Appointments
Hospitals OPDs : Locations & Directions
Jupiter Hospital (Baner)

Address
Lane 3, Baner- Balewadi Road,
Prathamesh Park,
Baner, Pune 411 045
Monday to Saturday 11 AM to 4 PM
Appointments
Contact us
Dr Anand Jadhav has a centralised appointment system for all locations across various hospitals and clinics in Pune & PCMC areas
Appointment Bookings & Requests can be made by any method :